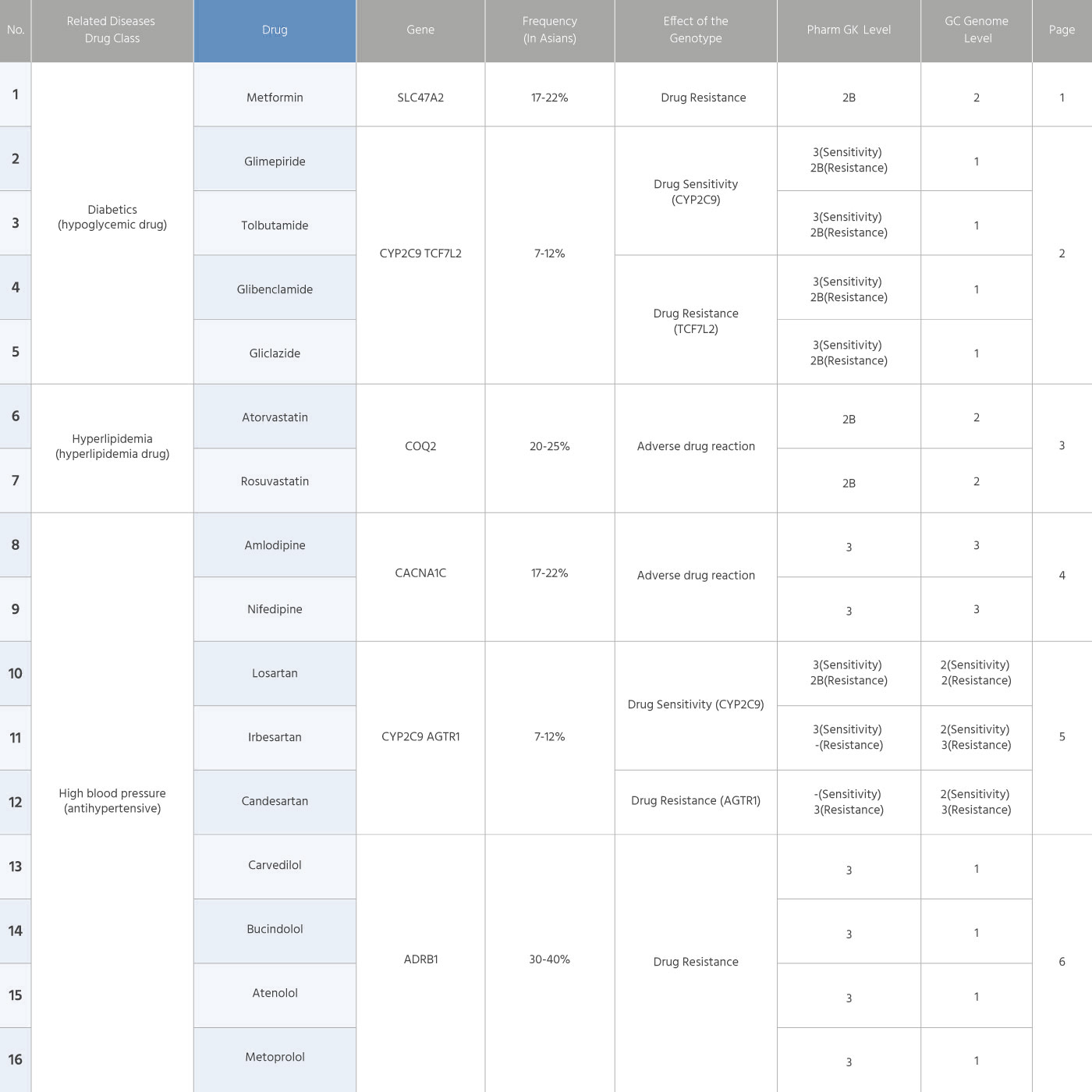
Pharmacogenetic Test
A Simple Solution to SAFE and EFFECTIVE Medication

Based on the individual’s genotype,
the drug metabolism among patients can be different.
What is a pharmacogenetics test?
A pharmacogenetics test analyzes the genetic information of DNA in the blood of the treatment recipient to evaluate the metabolic rate, sensitivity and resistance of the drug, and can estimate the therapeutic effect and predict the incidence of adverse events.
The test results can be used to optimize drug selection after consulting with a physician. The test will prevent unexpected emergencies related to drug resistance or drug sensitivity.

Relationship between Drug and Gene
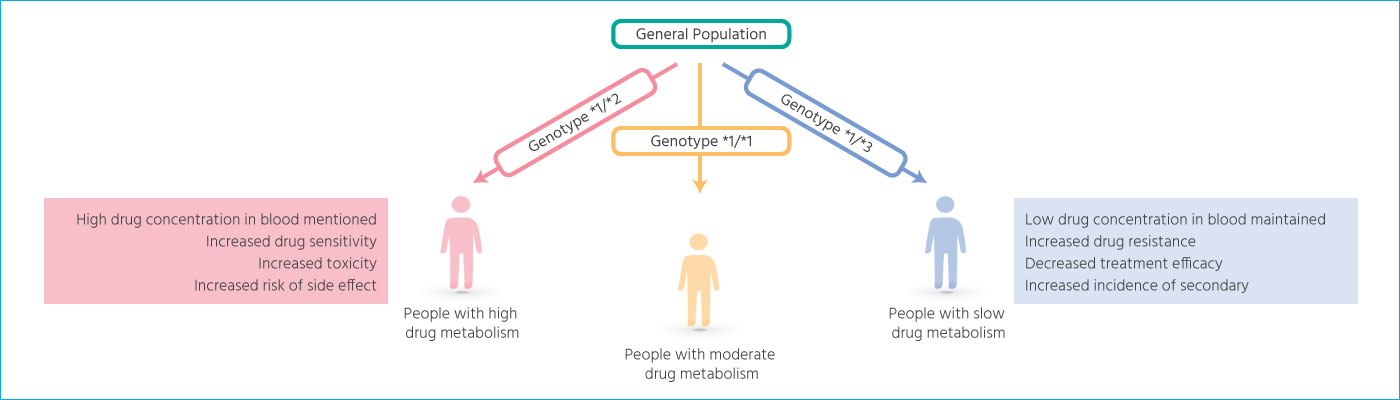
The same medicine may have a different therapeutic efficacy depending on the patient,
and some may not have an adequate therapeutic effect.
Pharmacogenetics testing propose safe and effective doses by genotyping tests
that indicate potential differences in drug responses.
Why should consider pharmacogenetics test?
Everyone response Differently to Drugs
Find out your compatbility with 34 common drugs that everyone is likely to take at least once in their lifetime
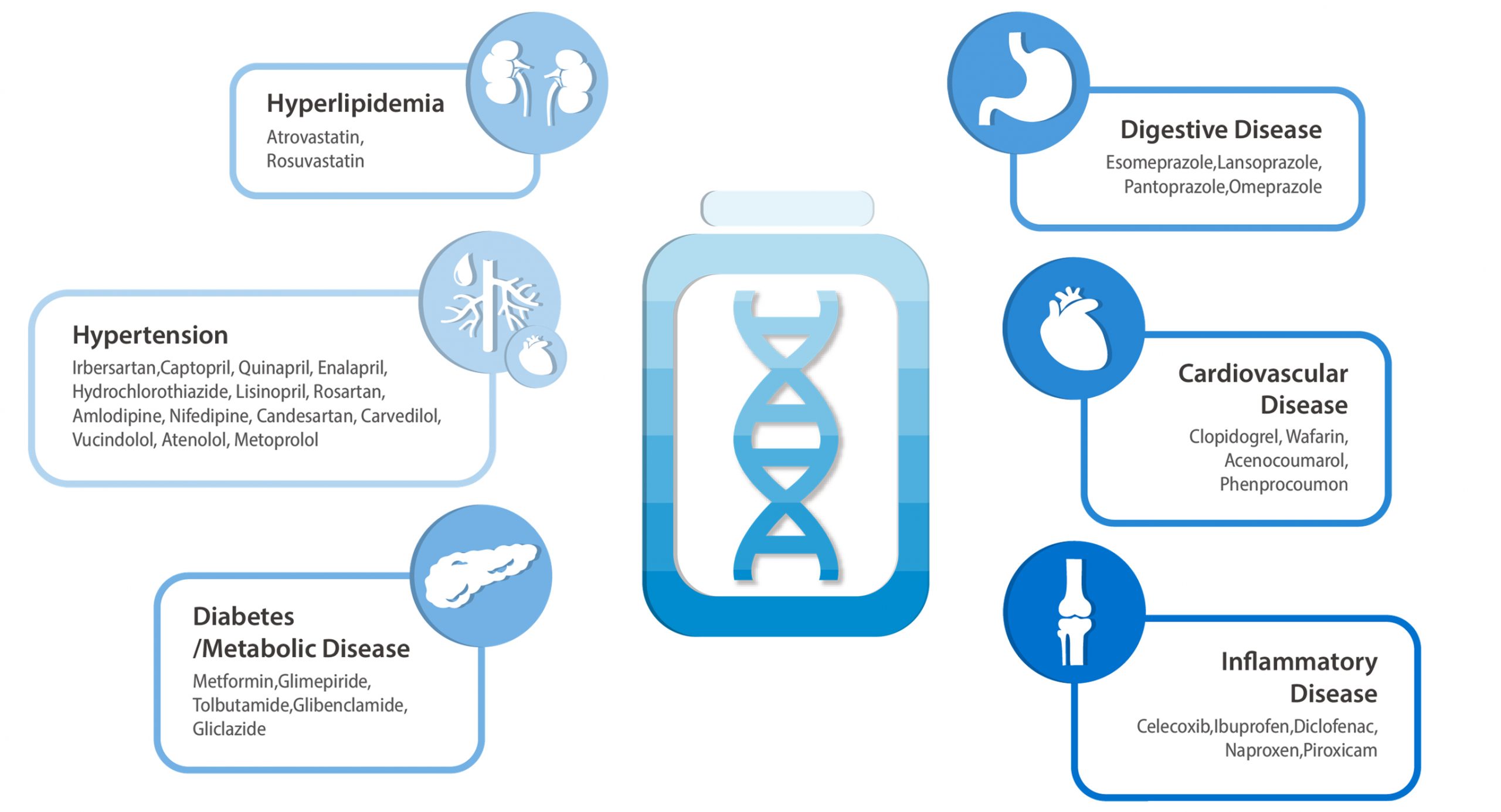
- Results of 34 commonly used medicines
- Systematic reviews of the literature and clinical guidelines for prescribing drugs according to the genotype
- Prevention of adverse drug reactions by genotype
- Prevention of indiscreet drug abuse
- Increased therapeutic effects by changing drugs or adjusting dosage
- Drug genotyping has to be done only once in a lifetime.
What is the key factor for the Pharmacogenetics test?
Provides Information for optimal medications to help save life and your pocket.
Information of 34 drug products
Drug sensitivity and drug resistance
For drug treatment, maintaining the drug’s blood concentration within normal parameters is important
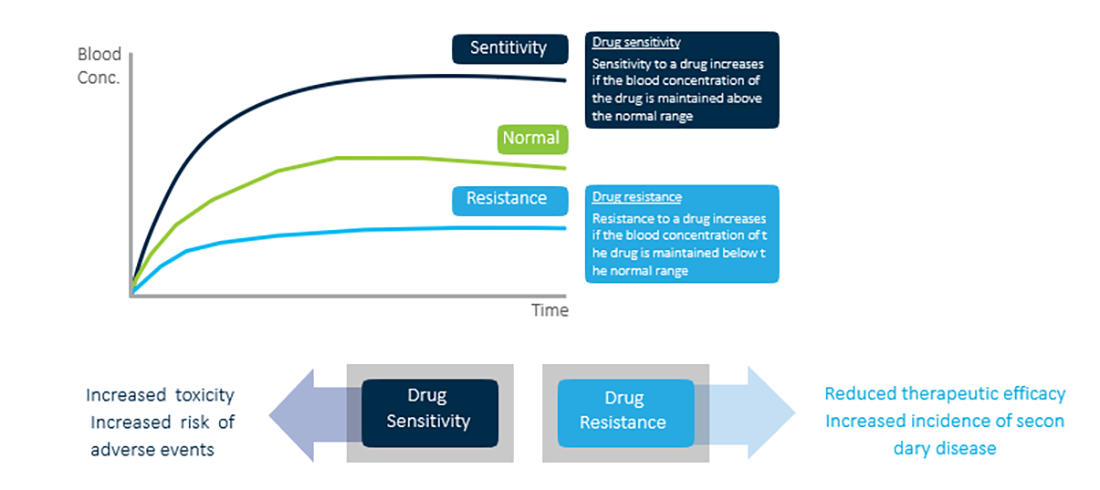
Drug sensitivity may increase the risk of toxic effects and the incidence of adverse events. It is the factor related to the decrease in the drug’s therapeutic efficacy and the incidence of secondary diseases. Therefore, there is a need to perform genotype screening for groups at high risk for drug sensitivity or drug resistance before prescribing safe and effective medications.
Notion of drug genotypes
For drug genotypes, the haplotype notation, HGVS notation in accordance with international standards and idiomatic notation that has been used for a long time are used together according to the characteristics of the subject gene.
| Notation method of drug genotypes | Subject Genes | Example and interpretation of notation |
|---|---|---|
| Haplotype | CYP2C9, CYP2C19 | CYP2C9 *1/*3 CYP2C9 = Name of the gene *1 = Normal haplotype / = Mark to delimit haplotype *3 = Variant haplotype (Numbers other than *1 means a variant haplotype.) |
| HGVS | ADRB1, AGTR1, CACNA1C, COQ2, NEDD4L, SLC47A2, RCF7L2 |
SLC47A2 c.-130TT SLC47A2 = Name of the gene c.-130 = Location of the genotype from the stand point of gene translation TT = Sequence pair located at c.-130 |
| Idiomatic Notation | ACE | ACE I/D (insertion/deletion genotype of the well-known intron 16 region of the ACE gene) ACE = Name of gene I = Insertion (insertion of the sequence in intron 16 region, academic idiomatic notation) / = Mart to delimit haplotype D = Deletion (deletion of the sequence in intron 16 region, academic idiomatic notation) |
PharmGKB literature assessment level
PharmGKB Level
PharmGKB is a highly reliable integrated database that provides important pharmacogenetic information and dose regimen recommendation guidelines, correlation between genotypes and phenotypes and related pharmacogenetic study results. It assesses drugs, classifying them by level 1A, 1B, 2A, 2B, 3 and 4 according to their importance. 1A is the highest literature assessment level and 4 is the relatively lowest level. However, it is necessary to consider some important clinical papers excluded from PharmGKB.
PharmGKB Level
We conducted clinical literature evidence assessment on 34 types of drugs included in the pharmacogenetics test, including important clinical papers excluded or omitted in the assessment. Our assessment levels are graded as Level 1, 2 and 3. Level 1 has 3 or more highly reliable published articles, level 2 has 2 or more highly reliable published articles and level 3 has only 1 highly reliable published article. The levels of published articles are the results of literature assessment for now, which can be changed according to the pharmacogenetic study results in the future.