SMN1, SMN2 Del/Dup Test
SMA diagnosis & carrier screening test
The faster the diagnosis is, the greater outcome is achievable.
Does it simply mean that the baby is developing a bit slowly?
Some symptoms may represent Spinal Muscular Atrophy.
What is Spinal Muscular Atrophy ?
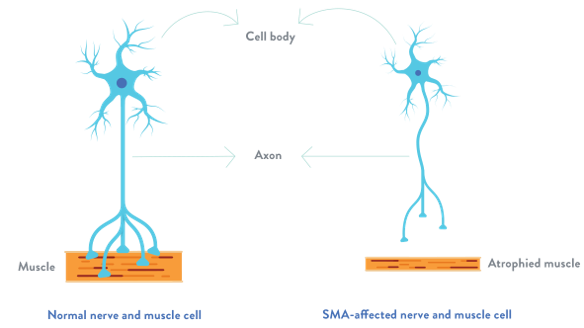
SMA (Spinal Muscular Atrophy) is a hereditary neuromuscular disorder caused by mutations in the SMN gene, which is responsible for maintaining motor neurons. Due to insufficient production of motor neurons, individuals with SMA experience genetic neuromuscular conditions.
In a healthy person, SMN gene produces a protein—called survival motor neuron protein or SMN protein—that is critical to the function of the nerves that control our muscles. Without it, those nerve cells cannot properly function and eventually die, leading to debilitating and sometimes fatal muscle weakness.
[The function of SMN gene]
SMN1
- Major gene produces SMN protein
- SMA occurs only when there are variants in both copies of the SMN1 gene.
SMN2
- Minor gene produces SMN protein
- Only 10% of produced SMN protein function normally
- All SMA patients have one or more SMN2 genes, and the number of SMN2 genes varies among individuals.
- The more the number of SMN2 genes, the less severe the symptoms tend to appear.
What is SMN1, SMN2 del/dup test ?
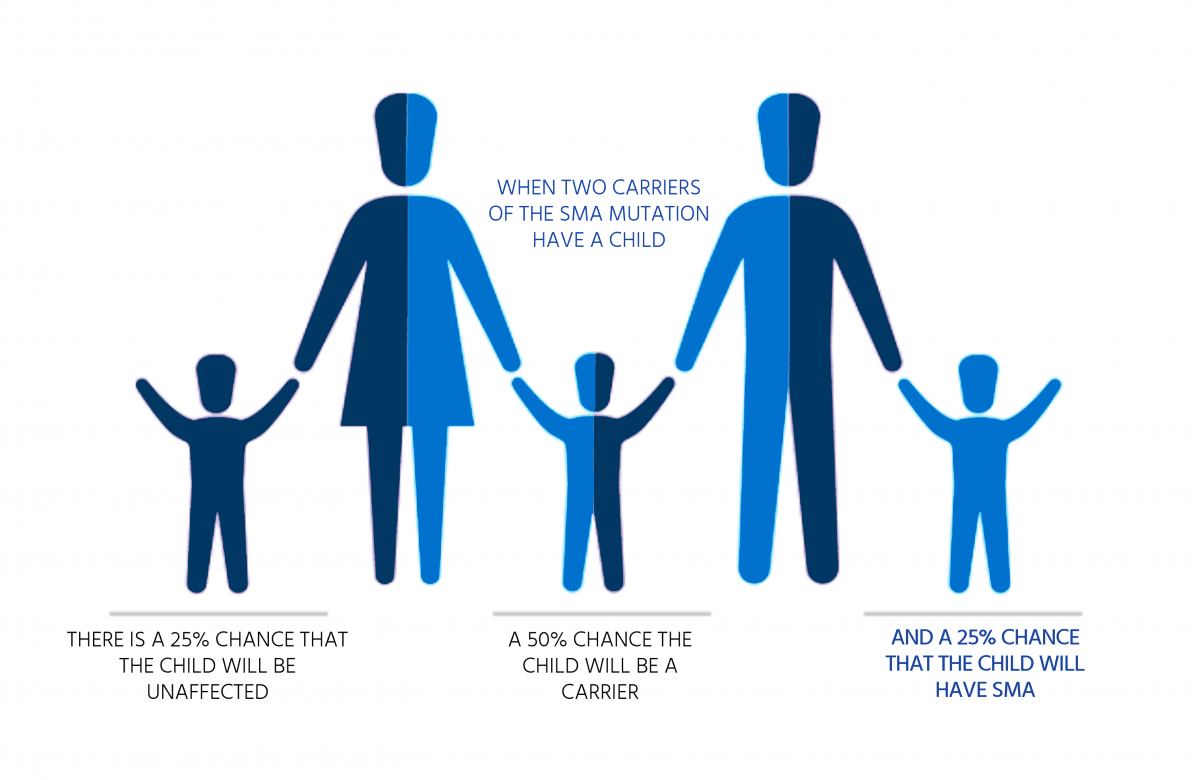
Among the SMN1 and SMN2 genes associated with this disease, the SMN1 gene is a major gene related to disease development.
95% of patients are homozygous for the SMN1 gene deletion mutation, and the remaining 5% are heterozygous
for the deletion mutation and point mutation.
This test is a test to confirm deletion and duplication of exon 7 and 8 of SMN1&SMN2 genes using the MLPA
(Multiplex Ligation dependent Probe Amplification) method.
What is the symptoms of Spinal Muscular Atrophy?
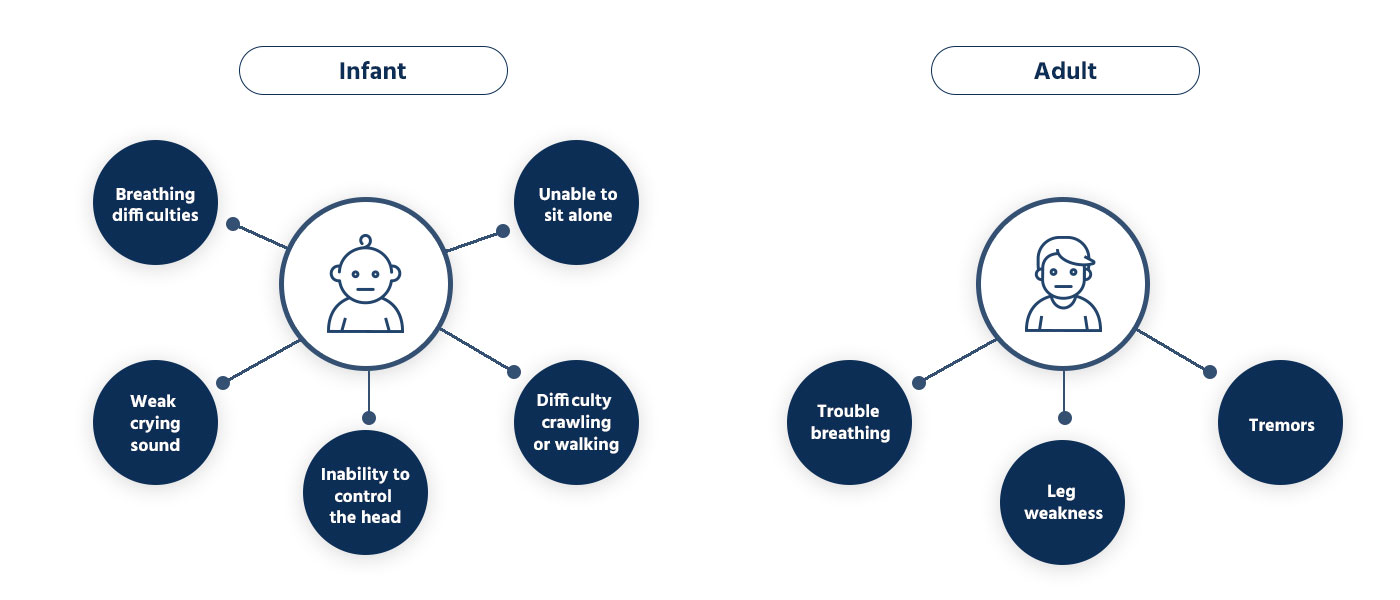
4 Types of Spinal Muscular Atrophy
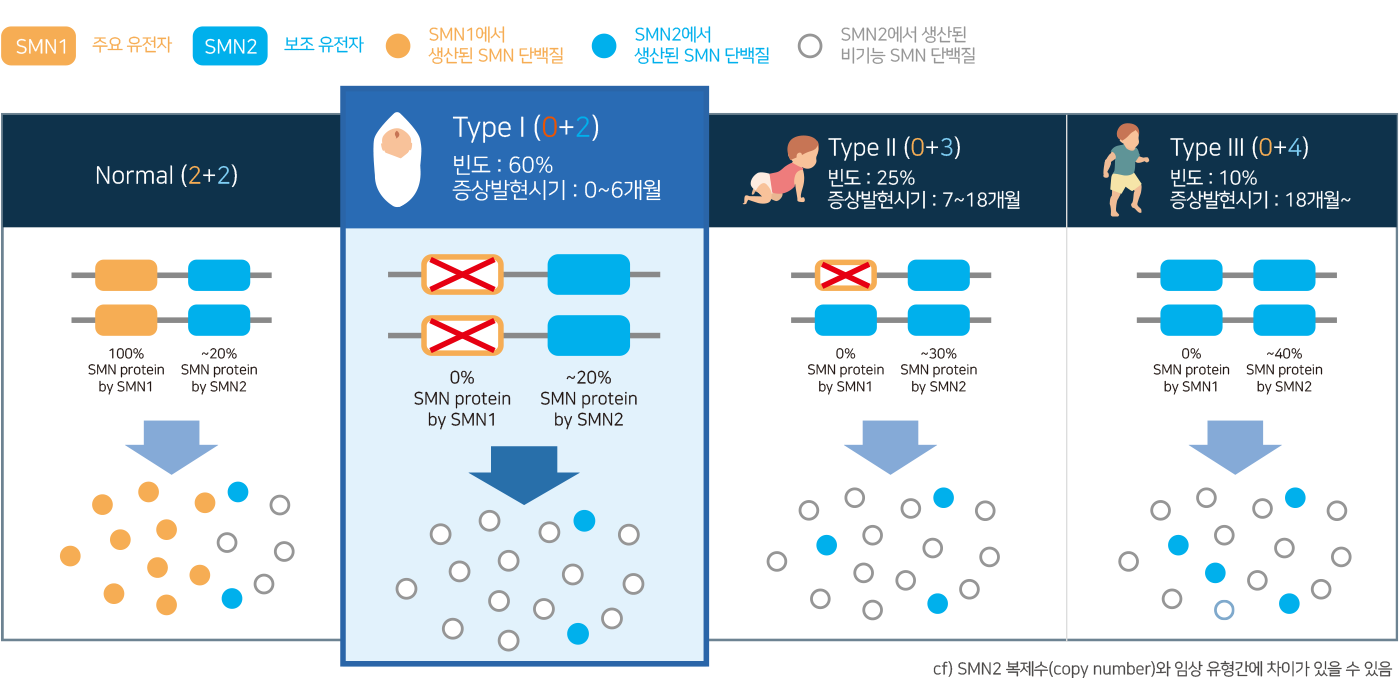
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is classified into several types based on the age of symptom onset, severity, variants and CNV of the SMN1 and SMN2 genes.
- Especially, SMA Type 1, also known as Werdning-Hoffman disease, is the most common type of SMA. It is characterized by significant symptoms and has the shortest life expectancy among the different types of SMA.
How does SMN work?
What is SMN1, SMN2 del/dup test ?
Among the SMN1 and SMN2 genes associated with this disease, the SMN1 gene is a major gene related to disease development. 95% of patients are homozygous for the SMN1 gene deletion mutation, and the remaining 5% are heterozygous for the deletion mutation and point mutation.
This test is a test to confirm deletion and duplication of exon 7 and 8 of SMN1&SMN2 genes using the MLPA (Multiplex Ligation dependent Probe Amplification) method.

Why SMN 1,2 for your patients?
Early diagnosis and prompt initiation of the treatment is a key factor affecting the treatment response.
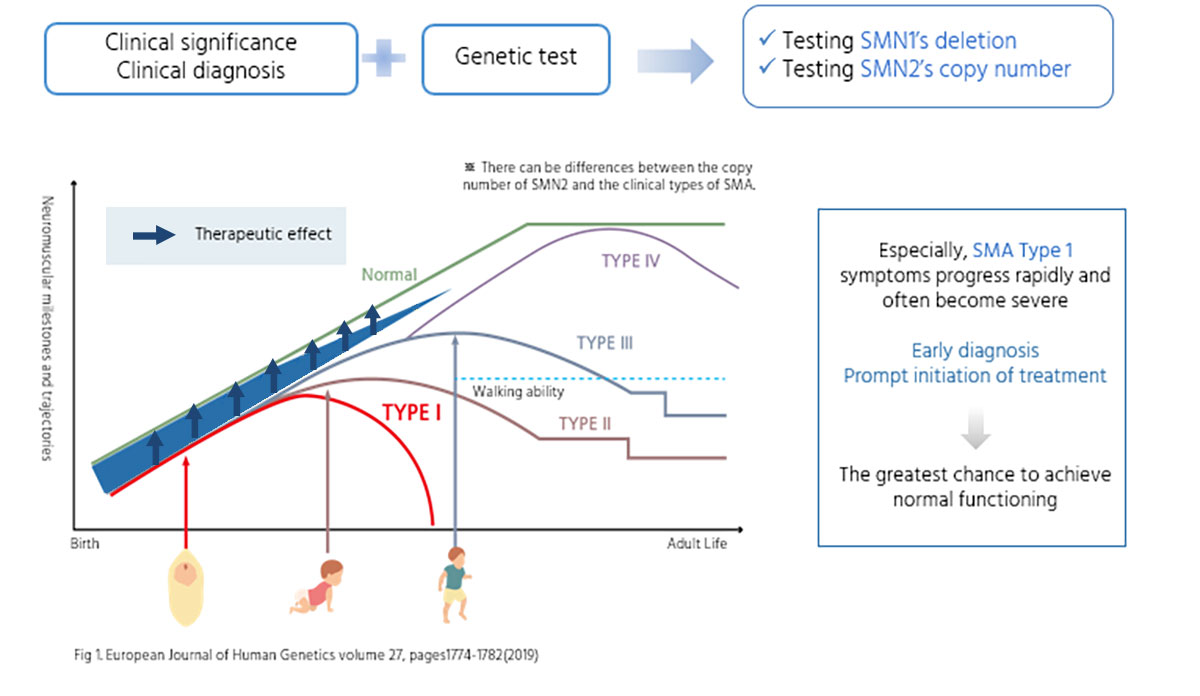
What is the next Process?
Various SMA treatments can be applicable based on the test results.
An accurate diagnosis through genetic testing is necessary to determine the use of therapies.
SPINRAZA® (nusinersen)
Spinraza is the intrathecal injection treatment for SMA. It is approved for use in pediatric and adult patients. It makes the SMN protein produced by the SMN2 gene functional. It works by fixing a mistake – RNA splicing error – that leads to exon 7 being skipped and a faulty protein being produced by SMN2. By rebinding at exon 7 – enhancing the inclusion of exon 7 into the SMN protein – the protein produced by SMN2 functions like that produced by SMN1.
Zolgensma® (onasemnogene abeparvovec-xioi)
Zolgensma is a gene therapy applicable for the infants before 2 years old. It prevents further motor neuron and muscle degeneration by replacing the defective or missing SMN1 gene.
Known formerly as AVXS-101, this one-time gene therapy treatment replaces the defective or missing gene (SMN1), which is responsible for making the survival motor neuron (SMN) protein. Providing a functional copy of SMN1 prevents motor neurons and muscles from degenerating further.
Evrysdi® (risdiplam)
Evrysdi is the first oral drug treatment for SMA. During SMN2 pre-mRNA splicing, it facilitates the highly specific inclusion of exon 7 in the mature transcript to enable production of sufficient functional SMN proteins amounts required to compensate for the loss of SMN1 function in SMA patients.



